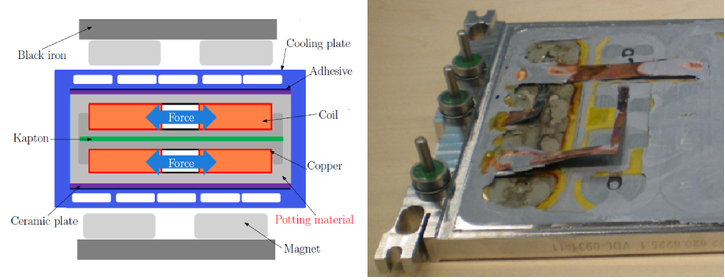
Actively cooled electromagnetic actuators, as used in for example the EUV lithography machines from ASML, are prone to failure by delamination of interfaces associated with the polymer-based potting material that serves both for heat conduction, load transfer and mechanical integrity of the actuator. The mechanisms of failure due to thermo-mechanical loads and the role of the microstructure of the potting material in these failure mechanisms are currently not well understood, which hampers the development of electromagnetic actuators with an economically viable and reliable lifetime.
The objective of this project is twofold: First of all, the project continues on a previous investigation of the microstructural characteristics of the potting material consisting of an epoxy matrix filled with several types of particulates via a variety of experimental techniques (e.g. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Computed Tomography (CT)). Key points of study are particle weight & volume fraction, morphology, orientation, segregation and the thermo-mechanical characteristics of potting material constituents as well as the complete potting material.
Figure 1: Schematic representation of an electromagnetic actuator cross-section and a picture of a segment of a failed actuator.
Second, the project considers an experimental exploration of crack surfaces and interfaces of the potting material itself and between the potting material and other actuator components over a range of length scales. For this, among others, samples of failed actuators will be used to conduct a post mortem analysis of these interfaces.