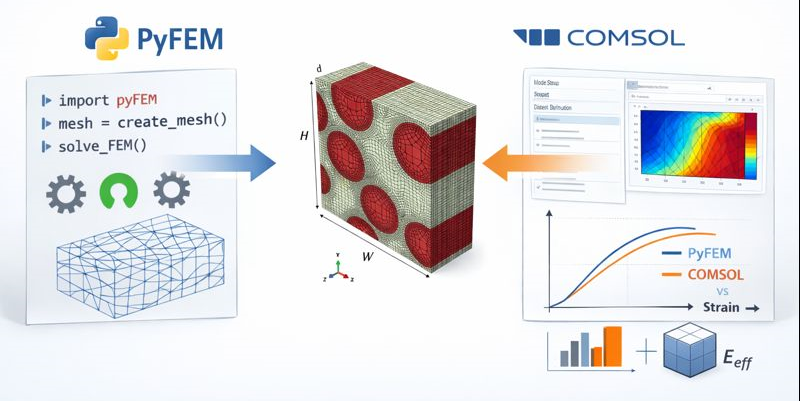
Computational modelling plays a key role in modern materials research, particularly when linking complex microstructures to macroscopic material behavior. Finite Element Method (FEM) tools are widely used for this purpose, ranging from open-source and research-driven codes to commercial multiphysics platforms. This Bachelor project aims to perform a systematic comparison between PyFEM, an open and extensible research-oriented finite element code, and COMSOL Multiphysics, a widely used commercial FEM package.
The project will focus on microstructural modelling of complex materials, such as heterogeneous solids or composite-like structures. Representative Volume Elements (RVEs) will be constructed and analyzed using both software environments. Various material models (e.g. linear elastic, nonlinear elastic, and inelastic constitutive laws) and element formulations will be considered, along with different homogenization techniques to extract effective macroscopic properties.
The comparison will address multiple aspects: numerical performance and computational efficiency, ease of model setup and user-friendliness, availability and flexibility of material models and element types, and post-processing and visualization capabilities. Special attention will be given to transparency, reproducibility, and extensibility—key aspects in academic research.
By the end of the project, you will have gained hands-on experience with advanced FEM modelling, microstructural analysis, and critical evaluation of simulation tools. The results will provide insight into the strengths and limitations of open research codes versus commercial software for materials science applications.